Pre and post request scripts
Ever wanted to use dynamic data in your request headers, URLs, before sending the request? Pre request scripts enables you do that. With pre request scripts, you can set environment variables from your cookies or create any combination of values for your environment variables. This comes in handy for environments where things like CSRF tokens are used to verify the requests sent to the server.
You might want to perform some extra logic with the response from a request. For example, setting an environment variable from a response header, or from the result of a query. Post request scripts enables you do just that.
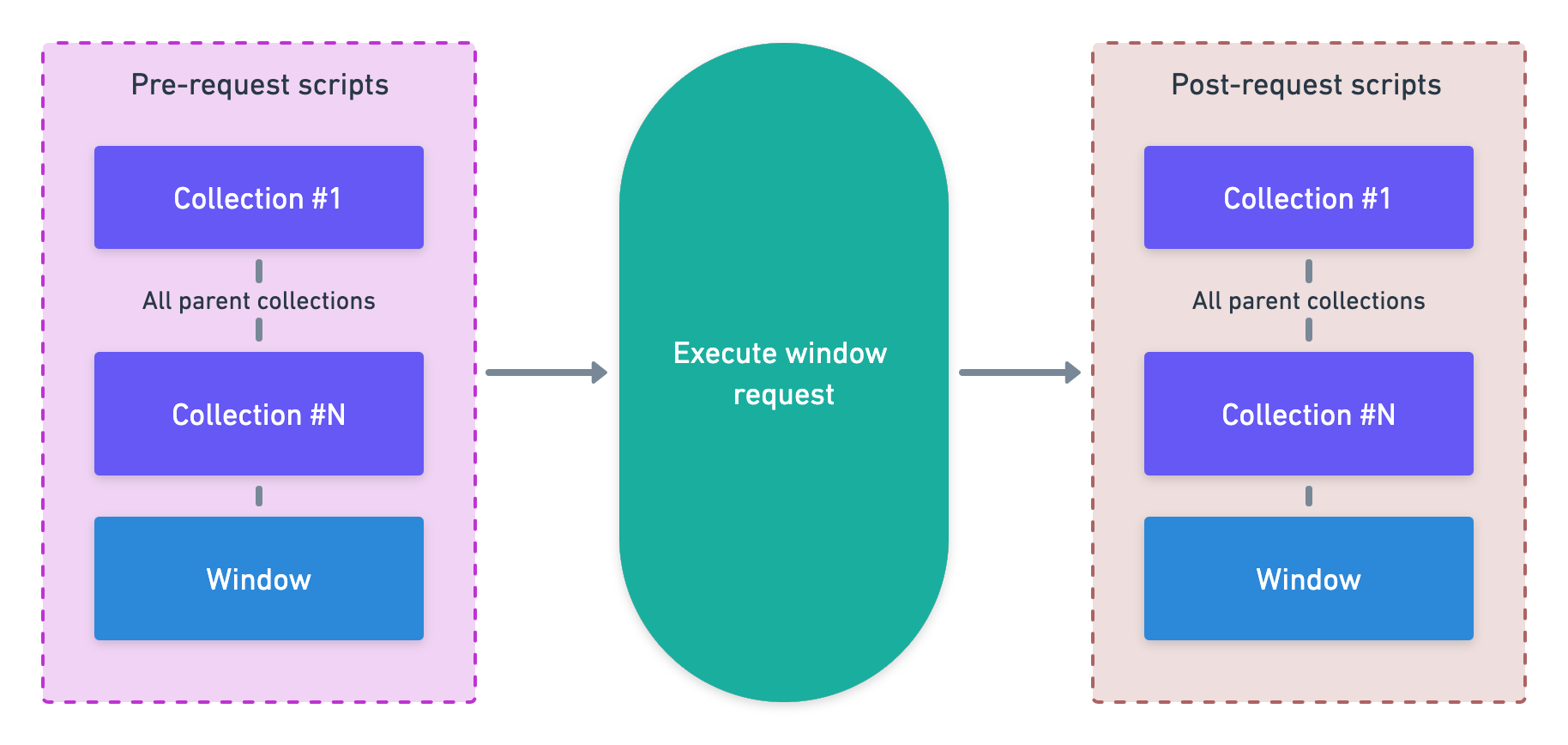
Execution order
Pre and post request scripts can be added to a query window, as well as to a collection. Also collections can be nested with sub collections as well. When a query that belongs to a collection is executed, the pre and post request scripts of the query window is executed as well as all the pre and post request scripts of the query's collection and all its parent collections. The execution order is as follows:
- Query collection pre request script
- All parent collections' pre request scripts
- Query window pre request script
- Execute query request
- Query collection post request script
- All parent collections' post request scripts
- Query window post request script
Note
You have to enable the request scripts in the window for any request scripts to be executed (including the request scripts in the collection).
Available API for request scripts
Request scripts support all JavaScript syntax supported in the latest ecmascript 2019 (ES10) specification (except with and label statements, but those are discouraged anyway). These include things like [].flat(), [].flatMap(), Object.fromEntries(), etc.
There is also a global object altair available within the context of the request script containing helper methods for interacting with altair.
altair.data
This contains data used to process your GraphQL request.
altair.data.headers - The headers sent as part of your request.
altair.data.variables - The parsed variables object sent as part of your request.
altair.data.query - The GraphQL query sent to the server.
altair.data.operationName - The GraphQL query operation name sent to the server.
altair.data.environment - The formatted environment object containing the serialized set of environment data before your request is sent.
altair.helpers
This contains a number of helper methods for carrying out basic tasks, like interacting with altair, making network requests, etc.
altair.helpers.getEnvironment(key: string) - Returns the environment variable for the specified key.
altair.helpers.getEnvironment('api_key');altair.helpers.setEnvironment(key: string, val: any, activeEnvironment?: boolean) - Sets the environment variable for the specified key, overriding the environment variable for the current request. You can also pass an extra boolean parameter to indicate if the environment variable should also be set in the currently active environment.
altair.helpers.setEnvironment('api_key', 'a482djksd289xxxxxxxxx');altair.helpers.getCookie(key: string) - Retrieves a value stored in browser cookie. You need to specify the list of cookies you want to grant access to in the pre request script in the script.allowedCookies settings.
const sessid = altair.helpers.getCookie('sessid');altair.helpers.request(...args)
const res = await altair.helpers.request(
'GET',
'https://api.agify.io/?name=michael'
);
// res => {"name":"michael","age":60,"count":41938}altair.storage
altair.storage.get(key: string): Promise<any> - Retrieves a value persisted in storage.
altair.storage.set(key: string, value: any): Promise<void> - Stores (persists) a value in storage for retrieval later.
Example Use Cases
Persisting data between requests
Since altair pretty much lives in a browser environment, it does support the LocalStorage feature. This is useful when you need an authentication token before each request but only requesting the token when your authentication expired.
Assuming you have this header in the Set Headers window:
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| Authorization | Bearer |
Below is a working example of pre-request script for persisting data between requests (token, token_expiry):
const nowInSeconds = () => Date.now() / 1000;
const tokenExpiry = (await altair.storage.get('token_expiry')) || 0;
if (nowInSeconds() >= Number(tokenExpiry)) {
// If the token expiry time has passed, fetch a new token from your auth server again (take note of the await)
const res = await fetch('https://auth.example.com', {
method: 'post',
headers: {
/* auth payload */
},
});
const data = await res.json();
// data => { "token": "abcd", "expiry": 3600 }
// Store the received token and expiry in localStorage
// Alternatively you can set this in the active environment
// altair.helpers.setEnvironment("token", res.token);
// altair.helpers.setEnvironment("token_expiry", nowInSeconds() + res.expiry);
await altair.storage.set('token', data.token);
await altair.storage.set('token_expiry', nowInSeconds() + data.expiry);
}
// Retrieve the token from localStorage
// const token = altair.helpers.getEnvironment("token");
const token = await altair.storage.get('token');
// Set the token as the `token_env` environment variable in Altair
altair.helpers.setEnvironment('token_env', token);
// You can use the environment variables in Altair after setting it by following this blog post: https://sirmuel.design/altair-becomes-environment-friendly-%EF%B8%8F-f9b4e9ef887caltair.response (Available in post request script)
This contains response from your GraphQL request. Note: This is only available in post request scripts.
altair.response.headers - The response headers sent from the server. Note: Due to some limitations on response headers in the browser, it is advisable to use the desktop apps if you need to use the response headers
altair.response.statusCode - The status code of the response.
altair.response.requestType - Indicates the type of request being sent. Values are query, introspection or subscription.
altair.response.responseTime - The total time of the request
altair.response.body - The response body
altair.importModule
This allows you to import some modules that are made available in the pre request script editor. It returns a promise that resolves with the imported module.
const btoa = await altair.importModule('btoa');
const res = btoa('username:password');The available modules are:
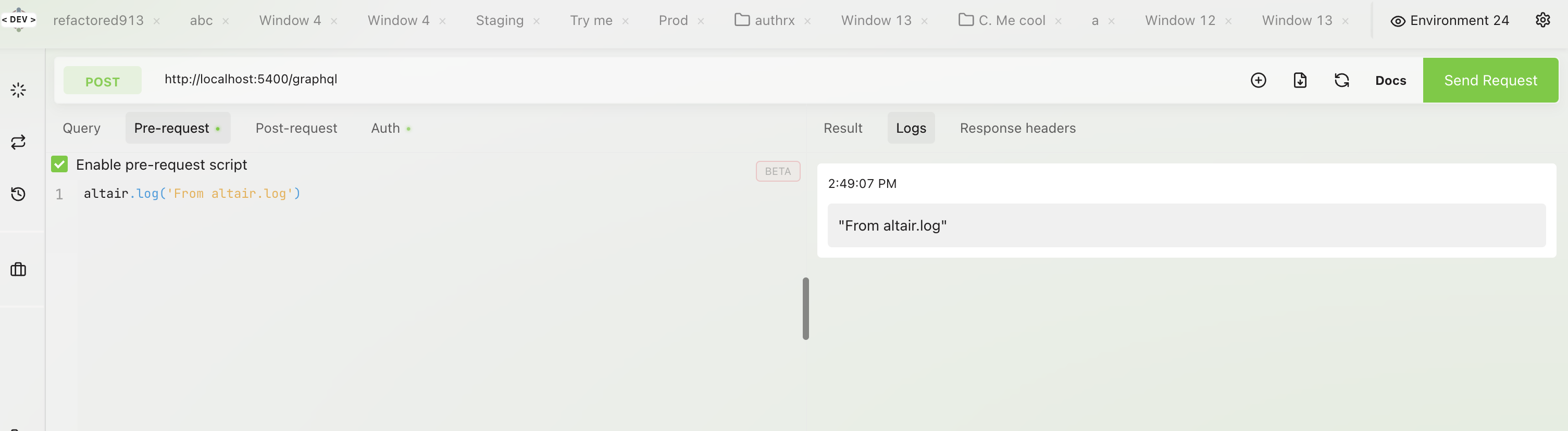
altair.log
Allows you to log an output from any of the request scripts to the Log tab. Usage: altair.log(myData).
 Altair GraphQL Client
Altair GraphQL Client